

if the knee "gives way" or feels unstable.the type of the activities (or sports) the person wants to do.Whether someone has surgery depends on many things, including: Some complete ACL tears will need surgery. A person might need to use crutches during recovery.

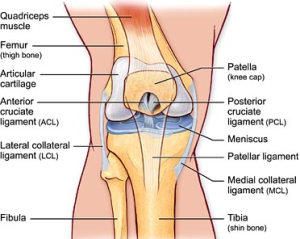
Most partial tears can be treated with bracing and physical therapy (PT). over-the-counter pain medicine such as acetaminophen (Tylenol or store brand) or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin, or store brand).RICE: Rest, Ice, Compression (with an elastic bandage), and Elevation (raising the knee).Right after the injury, an ACL tear is treated with: an MRI to check the extent of an ACL tear and to see if the knee has other injuries.X-rays to check for injuries to the bones.Imaging tests that might be done include: During the exam, the health care provider presses on the knee and legs and moves them in certain ways. To diagnose a torn ACL, health care providers ask about the injury and do a physical exam. How Is an Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear Diagnosed? This is most likely due to different anatomy. Women tear their ACL more often than men. Who Gets ACL Tears?ĪCL tears happen most often during sports involving turning, cutting, and pivoting like skiing, soccer, football, basketball, and tennis. The ACL also can tear if the knee is hit forcefully from the side. jumps and lands in a way that twists the knee.changes direction or twists the knee while running.Most ACL tears happen during athletic activity. But the knee may feel unstable and can "give way" and make the person stumble or fall. After the swelling goes down, someone with an ACL tear usually can walk. Their knee usually gets swollen soon after the injury. Most people who tear their ACL feel pain and a "pop" in their knee when the injury happens. What Are the Signs & Symptoms of an ACL Tear?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
